Biometric authentication is a security measure that utilizes unique biological characteristics or behavioral patterns of individuals to verify their identity. It is a form of identification and access control that relies on distinctive traits, such as fingerprints, facial features, iris or retinal patterns, voice, hand geometry, and even DNA. This advanced technology has gained popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness and convenience in various applications, including personal devices, corporate systems, and government facilities.
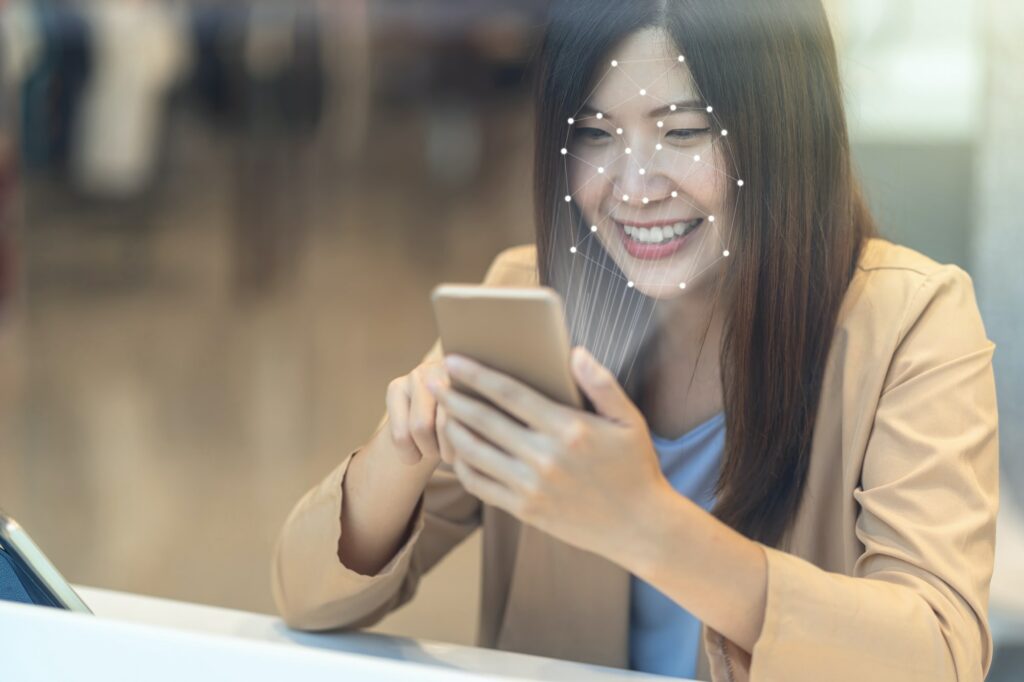

Table of Contents
ToggleHow biometric authentication works
Biometric authentication systems typically involve the following steps:
- Enrollment: During the enrollment process, an individual’s biometric data is recorded and stored securely in a database. This data is usually captured using specialized biometric sensors, scanners, or cameras, depending on the specific trait being measured.
- Extraction: When a person attempts to authenticate themselves using biometrics, the system captures their biometric data again. This data is then processed to extract the unique features or patterns that differentiate it from other individuals.
- Comparison: The extracted biometric data is compared to the stored reference data obtained during the enrollment phase. This matching process involves sophisticated algorithms that analyze and evaluate the level of similarity between the captured and stored biometric templates.
- Authentication: Based on the comparison results, the system determines whether the biometric traits presented match those on file. If there is a significant match, the individual is granted access or verified as the authorized user.
Advantages of biometric authentication
Biometric authentication offers several advantages over traditional identification methods:
- Security: Biometric traits are difficult to forge or replicate, providing a high level of security. Unlike passwords or PINs, which can be forgotten, stolen, or shared, biometric data is unique to each individual.
- Convenience: Biometric authentication eliminates the need for remembering complex passwords or carrying physical tokens, making it convenient for users. Individuals can simply present their biometric traits to gain access, saving time and effort.
- Accuracy: Biometric systems can achieve a high degree of accuracy in identifying individuals, reducing the risk of false positives or negatives. This reliability is crucial in sensitive environments where accurate identification is essential.
- Scalability: Biometric authentication can be easily scaled to accommodate a large number of users without compromising performance. It is particularly beneficial in organizations with numerous employees or in public settings where quick identification is necessary.
- Non-intrusiveness: Many biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or face recognition, are non-intrusive and require minimal physical contact, ensuring user comfort and ease of use.
Applications of biometric authentication
Biometric authentication finds applications in various fields, including:
- Personal Devices: Many smartphones, tablets, and laptops now incorporate biometric sensors, such as fingerprint scanners or facial recognition cameras, to enable secure and convenient device unlocking and data protection.
- Access Control: Biometric authentication is widely used in physical access control systems for buildings, airports, and other restricted areas. It enhances security by ensuring only authorized individuals can enter designated areas.
- Financial Transactions: Biometric authentication can provide secure authorization for financial transactions, such as withdrawing cash from ATMs or making payments. It adds an extra layer of protection against fraud and identity theft.
- Healthcare: Biometric systems are employed in healthcare settings to ensure accurate patient identification, secure medical records, and control access to sensitive areas, such as operating rooms or medication storage.
- Government Systems: Biometrics play a vital role in border control, passport issuance, voter registration, and law enforcement. They assist in enhancing national security, preventing identity fraud, and improving overall public safety.
Privacy and ethical considerations
While biometric authentication offers significant benefits, it also raises concerns regarding privacy and ethics. Biometric data, being inherently personal and unique, requires robust protection to prevent unauthorized access or misuse. Additionally, concerns exist regarding the potential for surveillance, data breaches, and the long-term storage and retention of biometric information.
To address these concerns, regulations and best practices are evolving to establish guidelines for the collection, storage, and usage of biometric data. Organizations and governments are encouraged to adopt transparent policies, informed consent practices, and stringent security measures to protect individuals’ privacy and uphold ethical standards.
Future developments
The field of biometric authentication continues to advance, with ongoing research and development focused on improving accuracy, usability, and security. Emerging technologies, such as behavioral biometrics (analyzing typing patterns, gait, or gestures) and multimodal biometrics (combining multiple traits for enhanced identification), show promise in further enhancing the effectiveness of biometric authentication.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms enables biometric systems to adapt and learn from new data, enhancing their performance over time. This continual refinement ensures biometric authentication remains at the forefront of secure identification and access control in the digital age.
Conclusion
Biometric authentication provides a robust and convenient method for verifying the identity of individuals. By utilizing unique biological traits or behavioral patterns, this technology offers enhanced security, accuracy, and user convenience across various applications. As biometric systems continue to evolve and address privacy concerns, they are likely to play an increasingly vital role in ensuring secure identification and access control in the future.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: Is biometric authentication more secure than traditional methods?
A: Yes, biometric authentication is generally considered more secure than traditional methods like passwords or PINs. Biometric traits are unique to each individual and difficult to forge or replicate, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access.
Q: Can biometric data be stolen or hacked?
A: While no security measure is entirely foolproof, biometric data is typically stored in encrypted and highly secure databases. Reputable organizations implement robust security measures to protect biometric information from theft or hacking. However, it’s essential to remain vigilant and choose trustworthy providers for biometric authentication systems.
Q: Can someone fake or spoof biometric traits?
A: Although some biometric traits can be spoofed, modern biometric systems employ advanced techniques to detect such attempts. For example, fingerprint scanners can identify fake fingerprints, and facial recognition algorithms can differentiate between a real face and a photograph or mask. Continuous advancements in biometric technology strive to enhance resistance against spoofing attacks.
Q: What happens if my biometric data is compromised?
A: In the event of a biometric data breach, the impact is different from a traditional data breach involving passwords or credit card information. Biometric data, such as fingerprints or iris patterns, cannot be changed like a password. However, reputable organizations take measures to protect biometric data and may have contingency plans in place to mitigate the risks associated with compromised data.
Q: Can biometric authentication systems be fooled by identical twins or close family members?
A: Biometric systems are designed to identify unique characteristics within individuals, including subtle differences even among identical twins. While some biometric traits may exhibit similarities between family members, modern systems incorporate sophisticated algorithms that can differentiate between individuals based on minute details, ensuring accurate identification.
Q: Is biometric authentication widely accepted and regulated?
A: Biometric authentication has gained widespread acceptance and is regulated in many industries and sectors. Governments and organizations have implemented regulations and standards to ensure the responsible use and protection of biometric data. However, the specific regulations may vary across jurisdictions, so it’s important to adhere to local laws and guidelines.
Q: Are there any limitations or challenges with biometric authentication?
A: Biometric authentication, like any technology, has certain limitations and challenges. Factors such as environmental conditions, injuries to biometric traits, or aging can impact recognition accuracy. Additionally, concerns regarding privacy, data protection, and ethical considerations associated with collecting and storing biometric data need to be addressed to maintain public trust in these systems.
Q: Can I use multiple biometric traits for authentication?
A: Yes, many systems support multimodal biometrics, which involve combining multiple biometric traits for enhanced identification. This can improve accuracy and security by incorporating, for example, fingerprint and facial recognition or voice and iris recognition. Multimodal biometrics provide an additional layer of robustness and flexibility in authentication systems.

